Via - National Geographic
A new study published in the journal Nature Communications, based on satellite imagery and other data from 1993 and 2009 maps the human footprint in those years. The good news is that the human footprint has not grown in direct proportion to population or the economy. However, some of the most intense pressure on the planet is being felt in places with the highest diversity of plant and animal life.
The above map shows the current footprint with the least impacted areas in blue and the most impacted in yellow and red. The map below shows the change in our impact on the planet between 1993 and 2009. Some of the wealthier areas have seen improvements but many of these are also areas that are already highly impacted.
The National Geographic article discusses how we can help save our biodiversity by focusing protection efforts on species-rich areas such as the Amazon Basin that are seeing significant impact. There are also links to the Wildlife Conservation Society's interactive maps where you can see the current footprint and change for any chosen area.
In the above change map areas of increasing pressure on the environment are in red and decreasing pressure is in blue. Areas not colored have seen little change. Much the Midwestern farming areas have seen decreasing pressure while the red areas include outer suburbs and areas of resource exploitation such as natural gas fracking. Africa has seen a great increase in pressure in the semi-arid Sahel region. Europe has a bit of and east/west split with the east seeing increasing pressure.
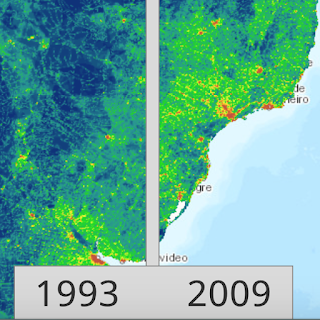
The other interactive map includes a slider where you can compare the human impact in 1993 and 2009 as shown here in southern Brazil and Uruguay.
These maps can be explored further by clicking on them or at this link.
A new study published in the journal Nature Communications, based on satellite imagery and other data from 1993 and 2009 maps the human footprint in those years. The good news is that the human footprint has not grown in direct proportion to population or the economy. However, some of the most intense pressure on the planet is being felt in places with the highest diversity of plant and animal life.
The above map shows the current footprint with the least impacted areas in blue and the most impacted in yellow and red. The map below shows the change in our impact on the planet between 1993 and 2009. Some of the wealthier areas have seen improvements but many of these are also areas that are already highly impacted.
The National Geographic article discusses how we can help save our biodiversity by focusing protection efforts on species-rich areas such as the Amazon Basin that are seeing significant impact. There are also links to the Wildlife Conservation Society's interactive maps where you can see the current footprint and change for any chosen area.
In the above change map areas of increasing pressure on the environment are in red and decreasing pressure is in blue. Areas not colored have seen little change. Much the Midwestern farming areas have seen decreasing pressure while the red areas include outer suburbs and areas of resource exploitation such as natural gas fracking. Africa has seen a great increase in pressure in the semi-arid Sahel region. Europe has a bit of and east/west split with the east seeing increasing pressure.
The other interactive map includes a slider where you can compare the human impact in 1993 and 2009 as shown here in southern Brazil and Uruguay.
These maps can be explored further by clicking on them or at this link.





No comments:
Post a Comment